This indicator describes changes in the chemistry of the ocean that relate to the amount of carbon dioxide dissolved in the water. Ocean acidification the worldwide reduction in the pH of seawater as a consequence of the absorption of large amounts of carbon dioxide CO2 by the oceans.
Ocean Acidity Over The Past 25 Million Years And Projected To 2100 European Environment Agency
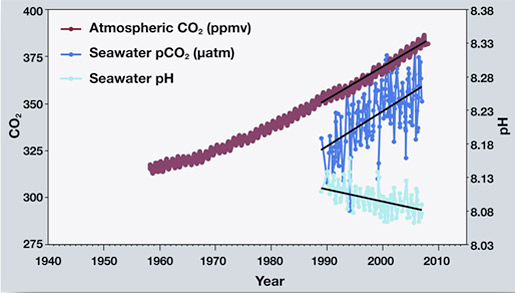
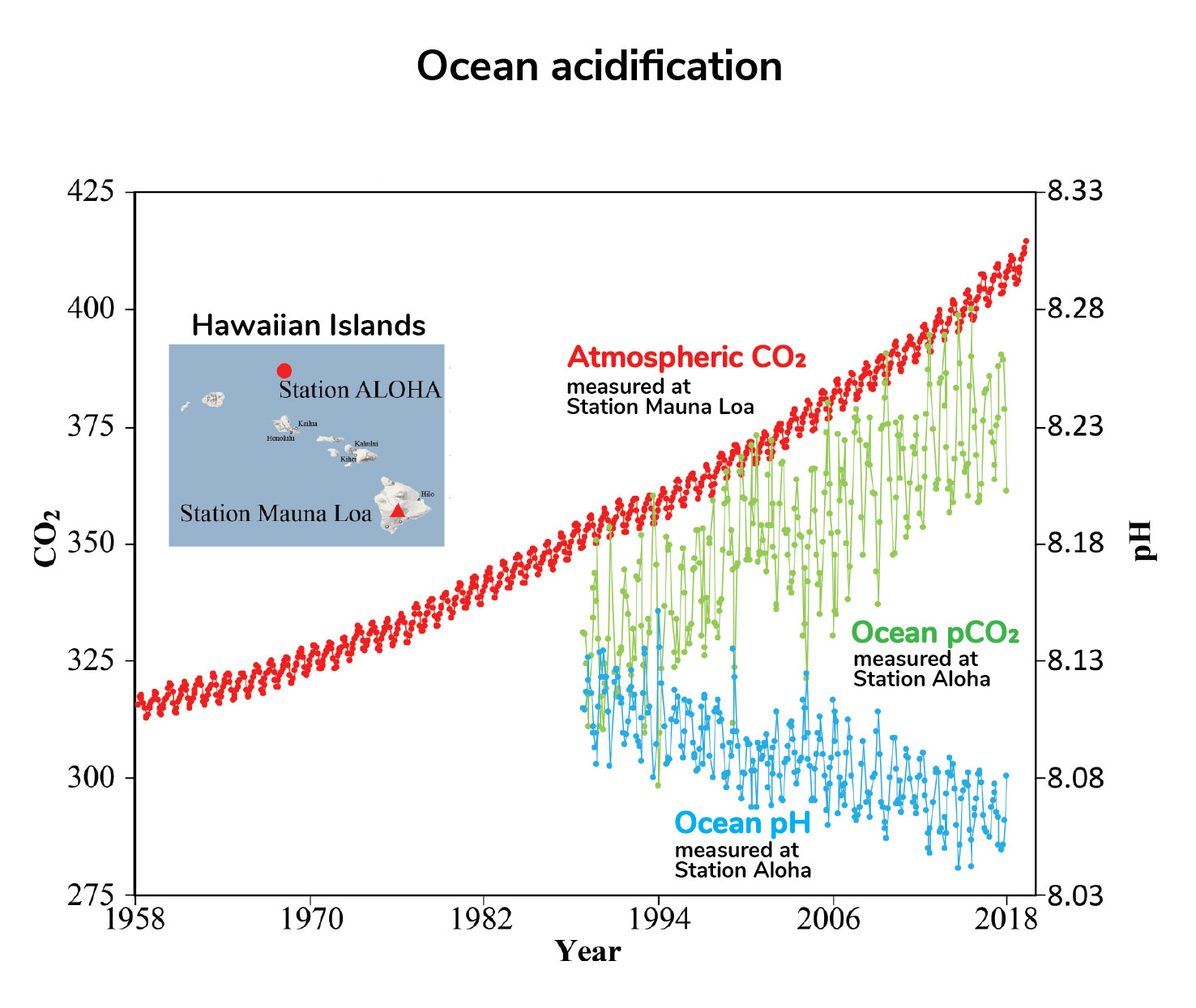
This figure shows the relationship between changes in ocean carbon dioxide levels measured in the left column as a partial.
. Ocean acidification is fundamentally changing the chemistry of the worlds oceans and threatening our marine resources. The result not surprisingly is that the ocean becomes more acidic upsetting the delicate pH balance that millions and millions of organisms rely on. How does it happen.
Climate Change Indicators. Oceanographers and marine biologists are now seeing a relationship between changes in ocean pH and carbon dioxide dissolved in sea water. That means ocean water is fairly neutral and slightly basic.
Understanding Ocean Acidification Learn how our oceans are absorbing increasingly more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere leading to lower pH and greater acidity. Future predictions indicate that the oceans will continue to absorb carbon. This resource explores the concept of changing pH linked to ocean acidification and can be used as a worksheet to aid understanding during the lesson or as homework.
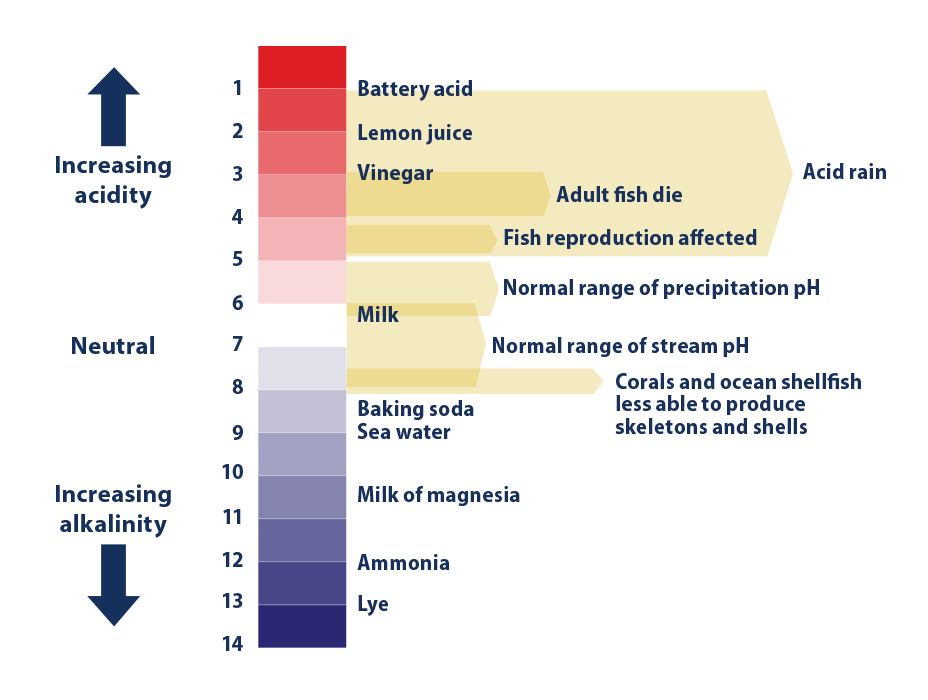
Acidity is a measure in units of pH of the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution in this case ocean water. Ocean Acidification Overview Lesson 3 describes the ocean as a carbon sink that absorbs atmospheric carbon. Fossil fuel combustion and industrial processes release over six billion metric tons of carbon into the atmosphere each year.
The pH scale along the secondary y-axis is completed for you. The lower the pH the more acidic the. Watch our video for a quick overview.
This decrease in pH can impact the growth and survival of marine organisms which. Complete the legend black will represent ocean pH c. As you probably noticed in the list above ocean water has a pH of approximately 8.
What is Ocean Acidification. The synthesized information shows that pollution-affected respiration acidifies coastal oceans more than the uptake of anthropogenic carbon dioxide. The positive relationship between ocean acidification and pollution Mar Pollut Bull.
Because of human-driven increased levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere there is more CO 2 dissolving into the ocean. Ocean acidification another effect of global warming. Ocean acidity refers to the concentration of hydrogen ions in ocean seawater regardless of ocean pH which is fundamentally basic eg pH 7.
In the activity students develop and test a hypothesis about how acidic. The consequences of these greenhouse gas emissions are often discussed in terms of rising global temperatures but global. Ocean acidification refers to a reduction in the pH of the ocean over an extended period of time caused primarily by uptake of carbon dioxide CO 2 from the atmosphere.
This might not seem like much of a difference but the relationship between pH and acidity is not direct. Ocean acidification can lead to decreased production of the shells of shellfish and other aquatic life with calcium carbonate shells as well as some other physiological challenges for marine organisms. Today average ocean pH is about 81.
Since the pH scale like the Richter scale is logarithmic this change represents approximately a 30 percent increase in acidity see our pH primer web page for more information. Each decrease of one pH unit is a ten-fold increase in acidity. Prior to the Industrial Revolution average ocean pH was about 82.
Draw a line on the graph to show the actual change in ocean pH over time. Since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution the pH of surface ocean waters has fallen by 01 pH units. Ocean acidification threatens corals and shellfish.
Ocean acidification refers to decreasing levels of pH in the ocean which makes the sea more acidic. Since the Industrial Revolution our seas have become about 30 percent more acidic a. Ocean surface waters have become 30 more acidic over the last 150 years as they have absorbed large amounts of CO 2 from the atmosphere 66 and anthropogenically sourced CO 2 is gradually invading into oceanic deep waters.
However in the past 100-200 years scientists have observed that ocean water has become 30 percent more acidic. Extension questions provide more challenge and delve into. Decrease in the oceans pH levels caused primarily by increased carbon dioxide.
Acidity which is the amount of acid present in a solution is measured using the pH scale. Draw a black trend line on the map to show the long-term trend in ocean pH over time. Illustrate the Actual Change in Ocean pH.
Roughly 30 percent of human-made CO2 is absorbed by the oceans. EPAs Climate Change Indicators 2016. Ocean acidification is largely the result of loading Earths atmosphere with large quantities of CO2 produced by vehicles and industrial and agricultural processes.
Ocean acidification provides a useful and engaging context to explore your learners understanding of the pH scale. In the ocean the dissolved carbon dioxide interacts with the water making the water more acidic thereby reducing its pH. The worlds oceans are absorbing more carbon dioxide as shown by the three sets of measurements in this graph.
This means that the acidity of the ocean today on average is about 25 greater than it. Measurements made over the last few decades have demonstrated that ocean carbon dioxide levels have risen in response to increased carbon dioxide in the atmosphere leading to an increase in acidity that is a decrease in pH see Figure 1. Students read evidence that increasing carbon dioxide CO 2 levels in the ocean are correlated with decreasing ocean pH.
For millions of years the exchange of CO 2 between the surface of the ocean and the atmosphere remained constant. Human-caused emissions of carbon dioxide fundamentally change the. Ocean Carbon Dioxide Levels and Acidity 19832018.
Ocean acidity as measured by pH has increased by 30 since the industrial revolution and scientists predict pH will continue to change as increasing amounts of carbon dioxide are absorbed by oceans. What is ocean acidification. A lower pH data indicates the ocean is becoming more acidic whereas a higher pH indicates the ocean water is becoming less acidic.
Coastal regions are more vulnerable to the. Currently about a third of the increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide is absorbed by the ocean. National What is ocean acidification.
More carbon dioxide means increased acidity lower pH. The oceans average pH is now around 81 offsite link which is basic or alkaline but as the ocean continues to absorb more CO 2 the pH decreases and the ocean becomes more acidic. Since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution about.
As you watch the interactive click forward note that each data set shows considerable variability in yearly measurements but when this variability is averaged over time definite trends can be observed. While this is beneficial in terms of limiting the rise in atmospheric CO 2 concentrations and hence greenhouse warming due to this CO 2 there are direct consequences for. It is the long-term change in seawater chemistry due to the absorption of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Ocean acidification is driven by increasing carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Ocean acidification will result in a shift towards a lower pH value meaning the water will become less basic and therefore more acidic.

Climate Change Indicators Ocean Acidity Us Epa
0 Comments